Groonga 6.0.3 has been released!
Groonga 6.0.3 has been released!
How to install in each environment: Install
Changes
Here are important changes in this release:
- Supported command version 3.
- Improved performance about between() without indexes.
- Added
numberandtimeplugins. - Supported window function.
Supported command version 3
In this release, Groonga supports command version 3.
Groonga command supports revision by command version.
In the previous versions, output format is something like:
> status
[[0,1464342851.826973,0.0002036094665527344],{"alloc_count":273,"starttime":1464342849,"start_time":1464342849,"uptime":2,"version":"6.0.3","n_queries":0,"cache_hit_rate":0.0,"command_version":1,"default_command_version":1,"max_command_version":3}]
If you specify --comand_version 3, the format of response is changed to object literal:
> status --command_version 3
{"header":{"return_code":0,"start_time":1464342859.177147,"elapsed_time":0.0001118183135986328},"body":{"alloc_count":276,"starttime":1464342849,"start_time":1464342849,"uptime":10,"version":"6.0.3","n_queries":0,"cache_hit_rate":0.0,"command_version":3,"default_command_version":1,"max_command_version":3}}
select Users --request_timeout 5
It makes JavaScript friendly.
Improved performance about between() without indexes
In this release, performance of between() without indexes is improved.
Here is the schema for benchmark.
table_create Entries TABLE_NO_KEY
column_create Entries rank COLUMN_SCALAR Int32
In the above sample, we expects that sequential search is used.
There are four test cases. The number of records are different.
- 1,000
- 10,000
- 100,000
- 1,000,000
The sequential number is assigned as rank.
During benchmark execution, we applied between() for the following cases.
- 1000 (select the number of rank is greater than 500, less than 600)
- 10,000 (select the number of rank is greater than 5,000, less than 5,100)
- 100,000 (select the number of rank is greater than 50,000, less than 50,100)
- 1,000,000 (select the number of rank is greater than 500,000, less than 500,100)
Here is the query which is executed.
select Entries --cache no --filter 'between(rank, 500, "exclude", 600, "include")'
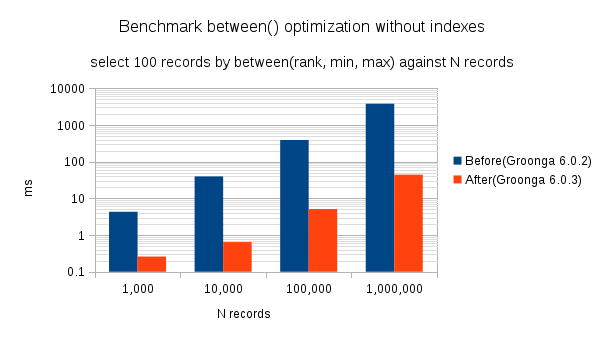
Here is the benchmark result. Note that median is used.
| Records | Groonga 6.0.2(ms) | Groonga 6.0.3(ms) |
|---|---|---|
| 1,000 | 4.3 | 0.2590 |
| 10,000 | 39.5 | 0.6440 |
| 100,000 | 390 | 5.1 |
| 1,000,000 | 3798.3 | 44.2 |
Here is the logarithmic graph. There is a great performance improvement.
Added number and time plugins
In this release, new plugins are added - time and number plugin.
It helps you to classify specific range of value as same value.
number plugin provies number_classify function.
Let's classify price every 100 value.
Here is the sample schema and data.
plugin_register functions/number
table_create Prices TABLE_PAT_KEY Int32
load --table Prices
[
{"_key": 0},
{"_key": 1},
{"_key": 99},
{"_key": 100},
{"_key": 101},
{"_key": 199},
{"_key": 200},
{"_key": 201}
]
Use the following query which uses number_classify:
select Prices --sortby _id --limit -1 --output_columns '_key, number_classify(_key, 100)'
number_classify(_key, 100) classifies the value by _key and classifies every 100.
[
[
[8],
[
["_key","Int32"],
["number_classify",null]
],
[0,0],
[1,0],
[99,0],
[100,100],
[101,100],
[199,100],
[200,200],
[201,200]
]
]
As every 100, data between 100 and 199 are treated as same range of price.
time plugin provides similar functionality about timestamp.
time plugin provides the following functions:
- time_classify_second
- time_classify_minute
- time_classify_hour
- time_classify_day
- time_classify_week
- time_classify_month
- time_classify_year
Next, classify timestamps every 10 minutes, here is the sample schema and data.
plugin_register functions/time
table_create Timestamps TABLE_PAT_KEY Time
load --table Timestamps
[
{"_key": "2016-05-05 22:29:59.999999"},
{"_key": "2016-05-05 22:30:00.000000"},
{"_key": "2016-05-05 22:30:00.000001"},
{"_key": "2016-05-05 22:39:59.999999"},
{"_key": "2016-05-05 22:40:00.000000"},
{"_key": "2016-05-05 22:40:00.000001"}
]
To classify every minute, use time_classify_minute function.
select Timestamps --sortby _id --limit -1 --output_columns '_key, time_classify_minute(_key, 10)'
Here is the result:
[
[
[6],
[
["_key","Time"],
["time_classify_minute",null]
],
[1462454999.999999,1462454400.0],
[1462455000.0,1462455000.0],
[1462455000.000001,1462455000.0],
[1462455599.999999,1462455000.0],
[1462455600.0,1462455600.0],
[1462455600.000001,1462455600.0]
]
]
The time interval is 10 minutes, data between 22:30 and 22:39 are treated as same range of timestamp (1462455000.0).
Supported window function
In this release, window function is supported.
For example, you can use record_number which returns nth number of record.
Here is the sample schema and data.
table_create Items TABLE_HASH_KEY ShortText
column_create Items price COLUMN_SCALAR UInt32
load --table Items
[
{"_key": "item1", "price": 666},
{"_key": "item2", "price": 999},
{"_key": "item3", "price": 777},
{"_key": "item4", "price": 111},
{"_key": "item5", "price": 333},
{"_key": "item6", "price": 222}
]
Let's search price data with nth number of record by ascending order. Here is the query for it.
select Items \
--columns[nth_record].stage initial \
--columns[nth_record].value 'record_number()' \
--columns[nth_record].type UInt32 \
--columns[nth_record].window.sort_keys price \
--output_columns '_key, price, nth_record'
The important point is that the value of record_number() is assigned to dynamic column nth_record.
[
[
[6],
[
["_key","ShortText"],
["price","UInt32"],
["nth_record","UInt32"]
],
["item1",666,4],
["item2",999,6],
["item3",777,5],
["item4",111,1],
["item5",333,3],
["item6",222,2]
]
]
It is obvious that each record is nth number of record.
Conclusions
Please refer to Release 6.0.3 - 2016-05-29 about detailed changes since 6.0.2.
Then, let's go all out to search by Groonga!