7.8.1. Summary#
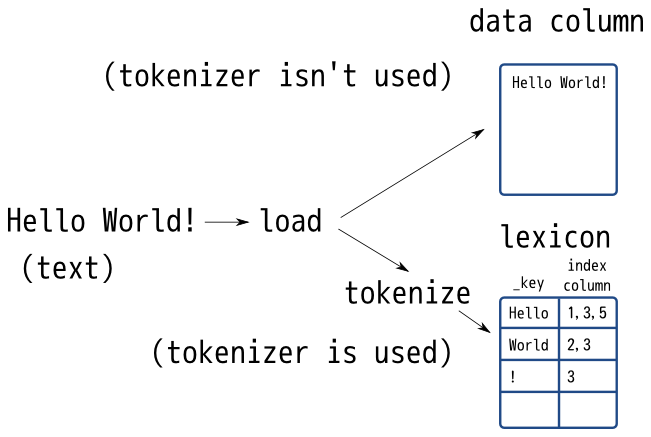
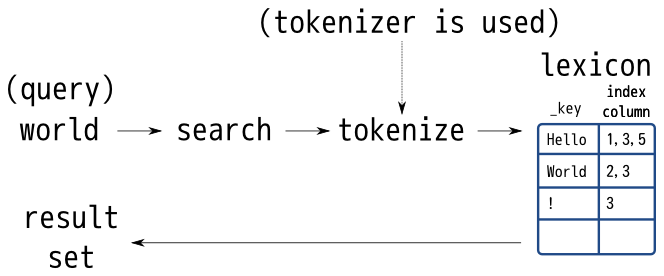
Groonga has tokenizer module that tokenizes text. It is used when the following cases:
Tokenizer is an important module for full-text search. You can change trade-off between precision and recall by changing tokenizer.
Normally, TokenBigram is a suitable tokenizer. If you don’t know much about tokenizer, it’s recommended that you choose TokenBigram.
You can try a tokenizer by tokenize and table_tokenize. Here is an example to try TokenBigram tokenizer by tokenize:
Execution example:
tokenize TokenBigram "Hello World"
# [
# [
# 0,
# 1337566253.89858,
# 0.000355720520019531
# ],
# [
# {
# "value": "He",
# "position": 0,
# "force_prefix": false,
# "force_prefix_search": false
# },
# {
# "value": "el",
# "position": 1,
# "force_prefix": false,
# "force_prefix_search": false
# },
# {
# "value": "ll",
# "position": 2,
# "force_prefix": false,
# "force_prefix_search": false
# },
# {
# "value": "lo",
# "position": 3,
# "force_prefix": false,
# "force_prefix_search": false
# },
# {
# "value": "o ",
# "position": 4,
# "force_prefix": false,
# "force_prefix_search": false
# },
# {
# "value": " W",
# "position": 5,
# "force_prefix": false,
# "force_prefix_search": false
# },
# {
# "value": "Wo",
# "position": 6,
# "force_prefix": false,
# "force_prefix_search": false
# },
# {
# "value": "or",
# "position": 7,
# "force_prefix": false,
# "force_prefix_search": false
# },
# {
# "value": "rl",
# "position": 8,
# "force_prefix": false,
# "force_prefix_search": false
# },
# {
# "value": "ld",
# "position": 9,
# "force_prefix": false,
# "force_prefix_search": false
# },
# {
# "value": "d",
# "position": 10,
# "force_prefix": false,
# "force_prefix_search": false
# }
# ]
# ]
“tokenize” is the process that extracts zero or more tokens from a text. There are some “tokenize” methods.
For example, Hello World is tokenized to the following tokens by
bigram tokenize method:
He
el
ll
lo
o_(_means a white-space)
_W(_means a white-space)
Wo
or
rl
ld
In the above example, 10 tokens are extracted from one text Hello
World.
For example, Hello World is tokenized to the following tokens by
white-space-separate tokenize method:
Hello
World
In the above example, 2 tokens are extracted from one text Hello
World.
Token is used as search key. You can find indexed documents only by
tokens that are extracted by used tokenize method. For example, you
can find Hello World by ll with bigram tokenize method but you
can’t find Hello World by ll with white-space-separate tokenize
method. Because white-space-separate tokenize method doesn’t extract
ll token. It just extracts Hello and World tokens.
In general, tokenize method that generates small tokens increases recall but decreases precision. Tokenize method that generates large tokens increases precision but decreases recall.
For example, we can find Hello World and A or B by or with
bigram tokenize method. Hello World is a noise for people who
wants to search “logical and”. It means that precision is
decreased. But recall is increased.
We can find only A or B by or with white-space-separate
tokenize method. Because World is tokenized to one token World
with white-space-separate tokenize method. It means that precision is
increased for people who wants to search “logical and”. But recall is
decreased because Hello World that contains or isn’t found.